最近碰到一个问题,在看<<快学Java8>>的时候,作者让写一段代码比较使用parallel stream和一般的stream的性能差异,书中说直接使用System.currentTimeMillis()记录时间,然后比较耗时长短,结果却发现执行相同的任务(统计<<战争与和平>>这本书中的长单词数量)并行流所花的时间居然比一般的流更长,这显然不符合预期。google之后,在StackOverflow看到一个人说那样测试性能不准确,他推荐使用JMH。改用JMH之后,我最终得到了期望的结果。
JMH是一个microbenchmark测试框架,是由OpenJDK的开发人员开发的,所以其结果具有很高的可信性,而且它用起来和JUnit一样的方便。下面是官方的hello world示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class JMHSample_01_HelloWorld {
@Benchmark
public void wellHelloThere() {
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws RunnerException {
Options opt = new OptionsBuilder()
.include(JMHSample_01_HelloWorld.class.getSimpleName())
.forks(1)
.build();
new Runner(opt).run();
}
}
|
这段代码中的main方法其实是多余的,我们可以通过annotation processor使得测试自动执行,这个之后会介绍。
环境搭建
首先,安装IDEA的JMH插件
然后,在项目的gradle配置文件中加上JMH的依赖
1
2
| testCompile 'org.openjdk.jmh:jmh-core:1.19'
testCompile 'org.openjdk.jmh:jmh-generator-annprocess:1.19'
|
注意,第二个依赖不能省略,它是JMH实现的自定义注解处理器,用于在IDE中运行JMH的测试。
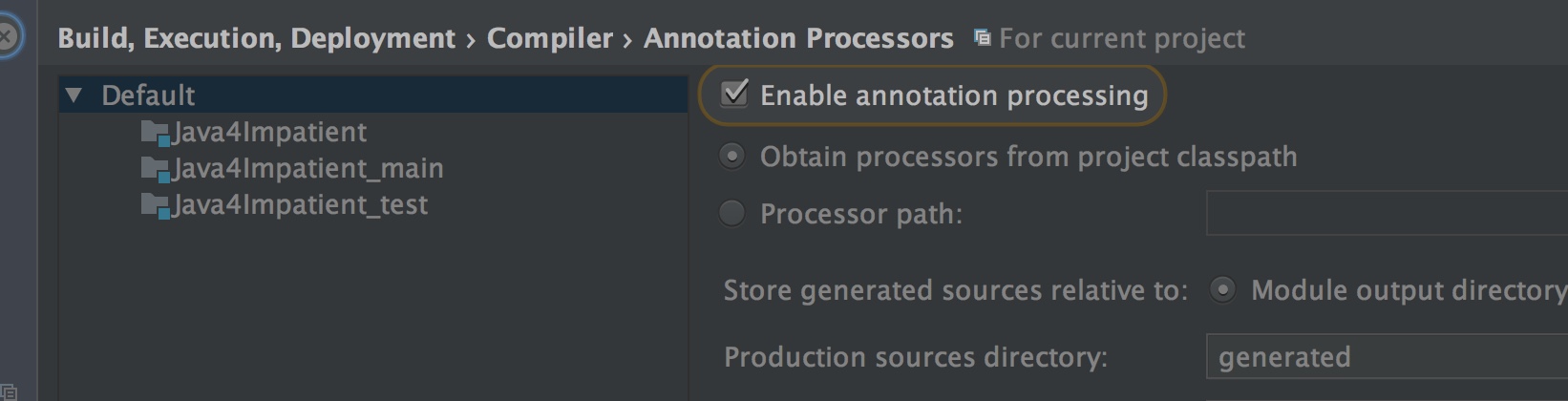
之后,查看IDEA的配置,确保annotation processor是启用的。在Eclipse中需要安装m2e-apt插件并启用。
## 一个简单的测试
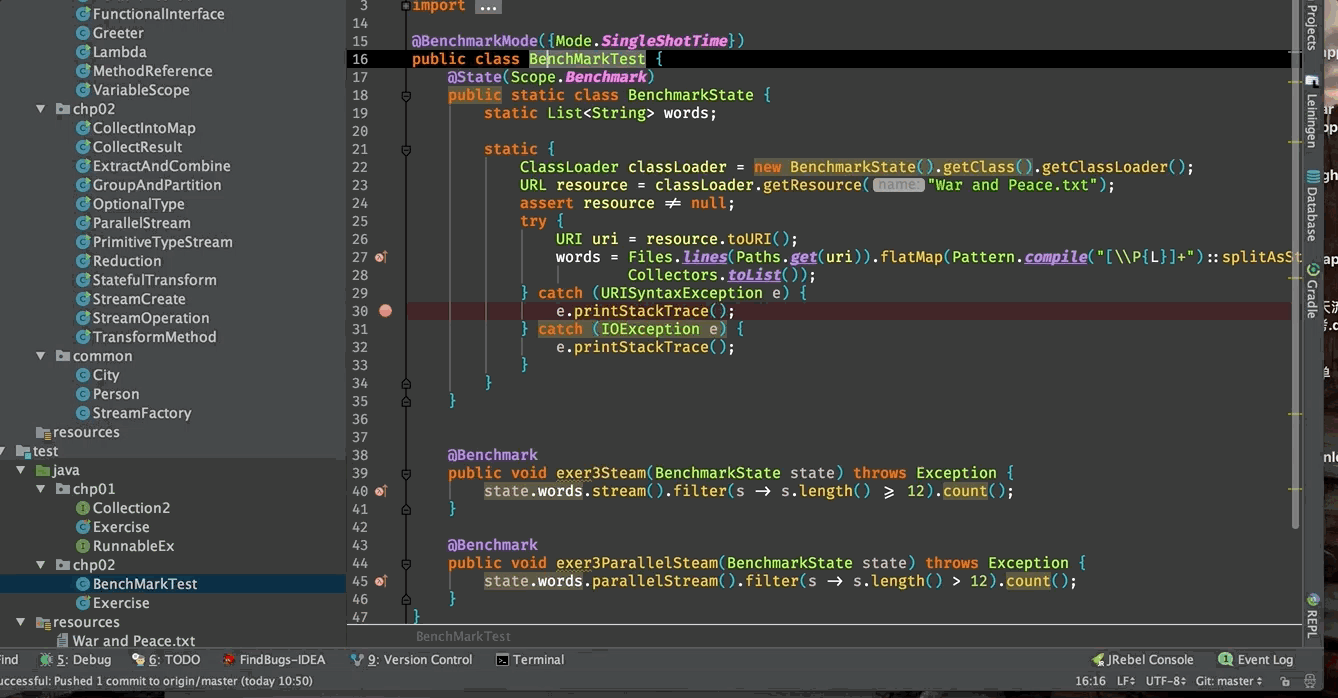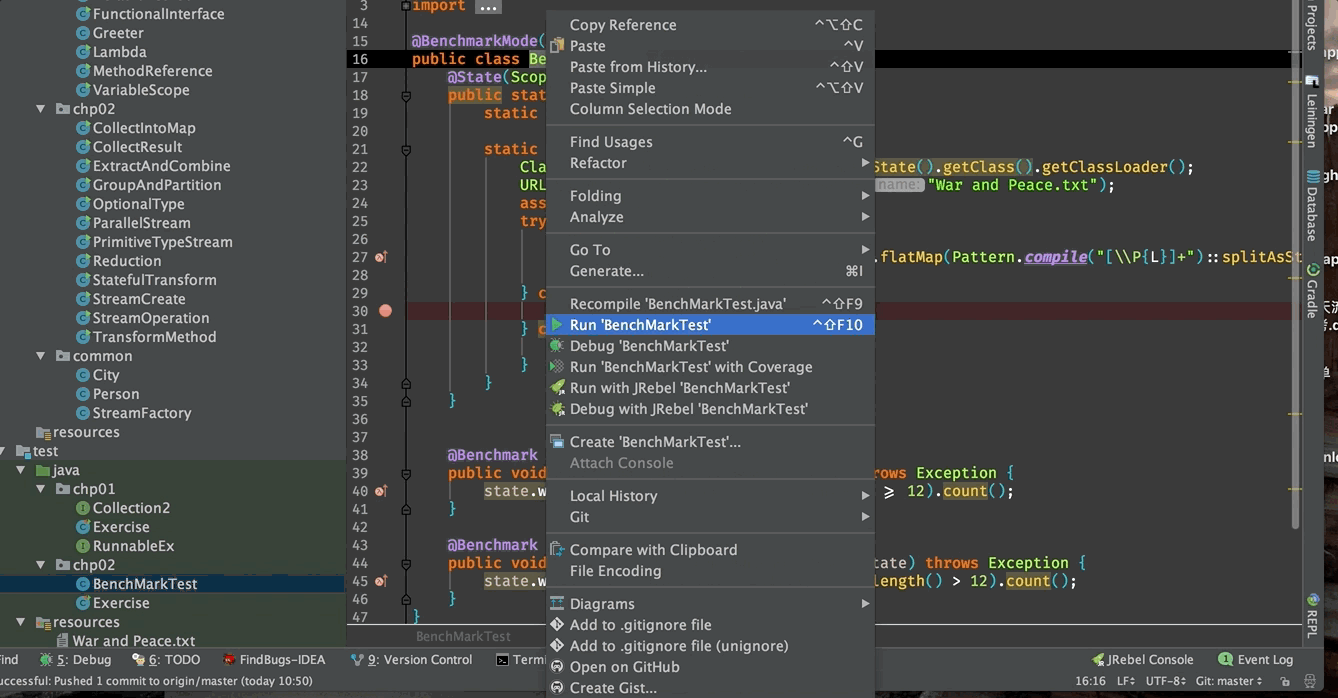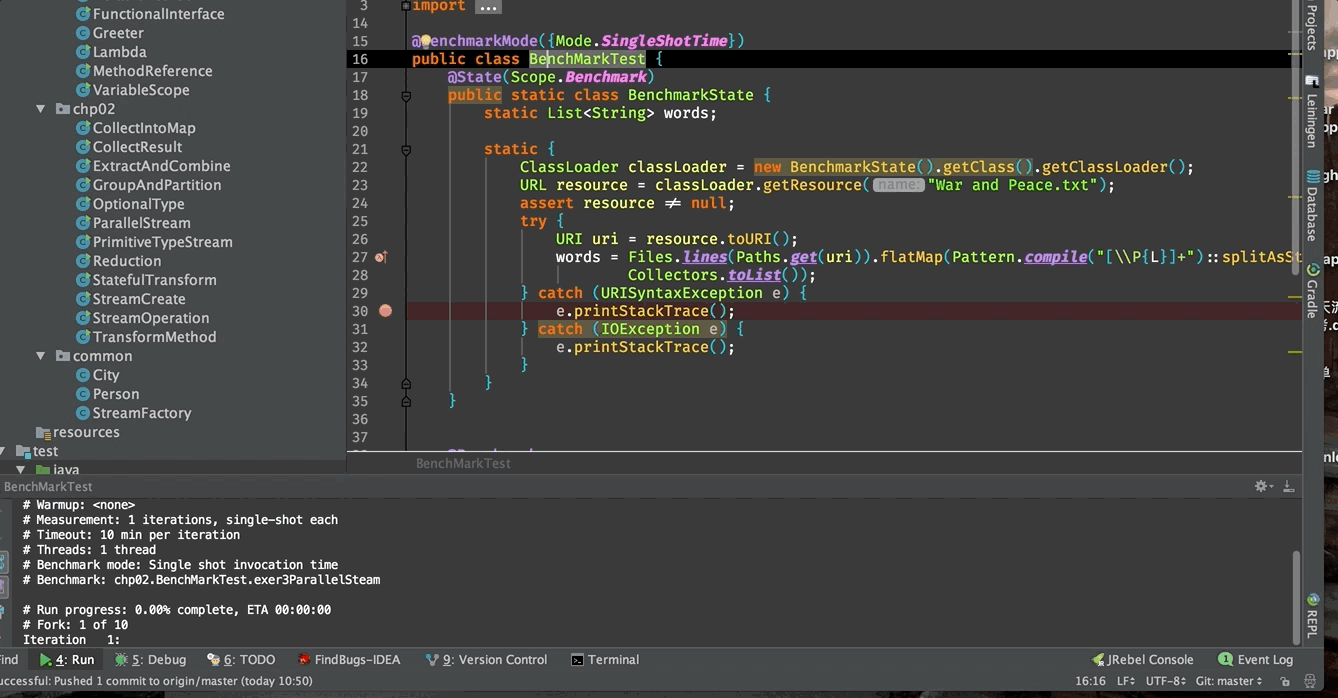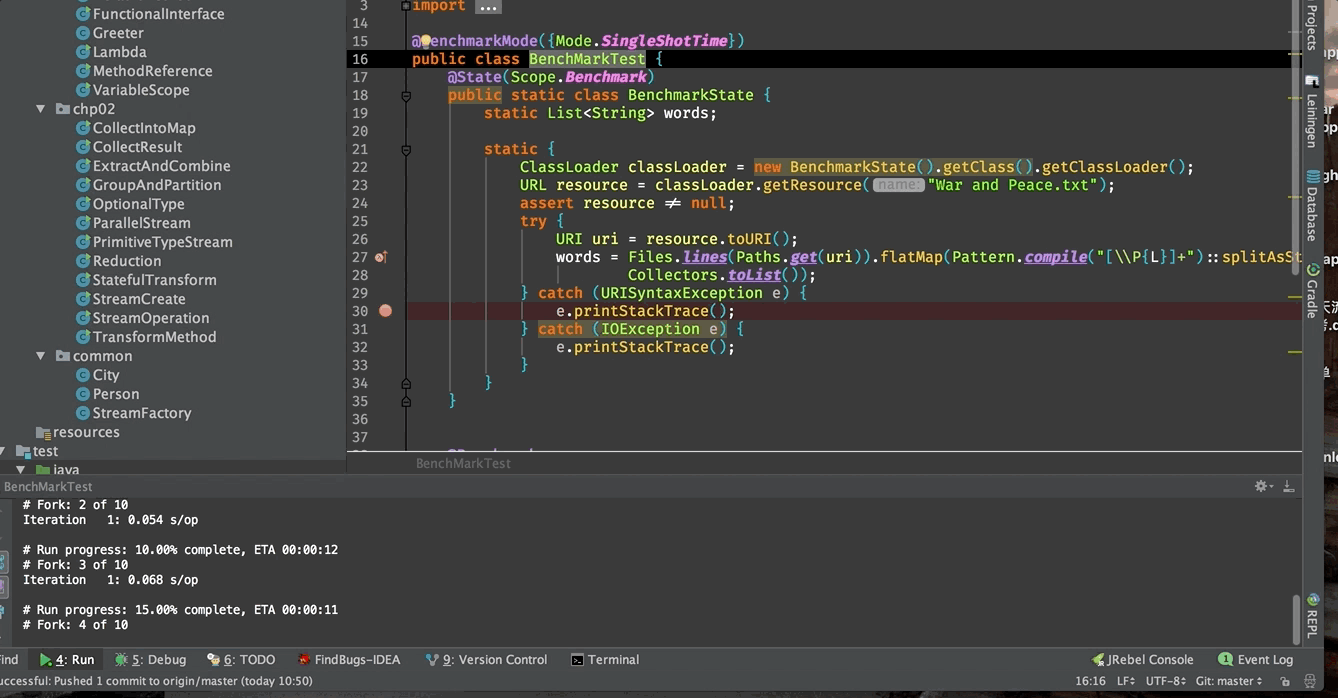
下面是促使我发现JMH的那个问题的代码,使用JMH重构过。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| @BenchmarkMode({Mode.AverageTime})
@Warmup(iterations = 5)
@Measurement(iterations = 10)
@Fork(10)
@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
public class BenchMarkTest {
@State(Scope.Benchmark)
public static class BenchmarkState {
static List<String> words;
static {
ClassLoader classLoader = new BenchmarkState().getClass().getClassLoader();
URL resource = classLoader.getResource("War and Peace.txt");
assert resource != null;
try {
URI uri = resource.toURI();
words = Files.lines(Paths.get(uri))
.flatMap(Pattern.compile("[\\P{L}]+")::splitAsStream)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Benchmark
public void exer3Steam(BenchmarkState state) throws Exception {
state.words.stream().filter(s -> s.length() >= 12).count();
}
@Benchmark
public void exer3ParallelSteam(BenchmarkState state) throws Exception {
state.words.parallelStream().filter(s -> s.length() > 12).count();
}
}
|
可以看出,JMH的测试方法是可以有参数的,其中一种就是有@State注解的类的实例。
然后把光标移动到类名或方法名上,右击并选择运行。
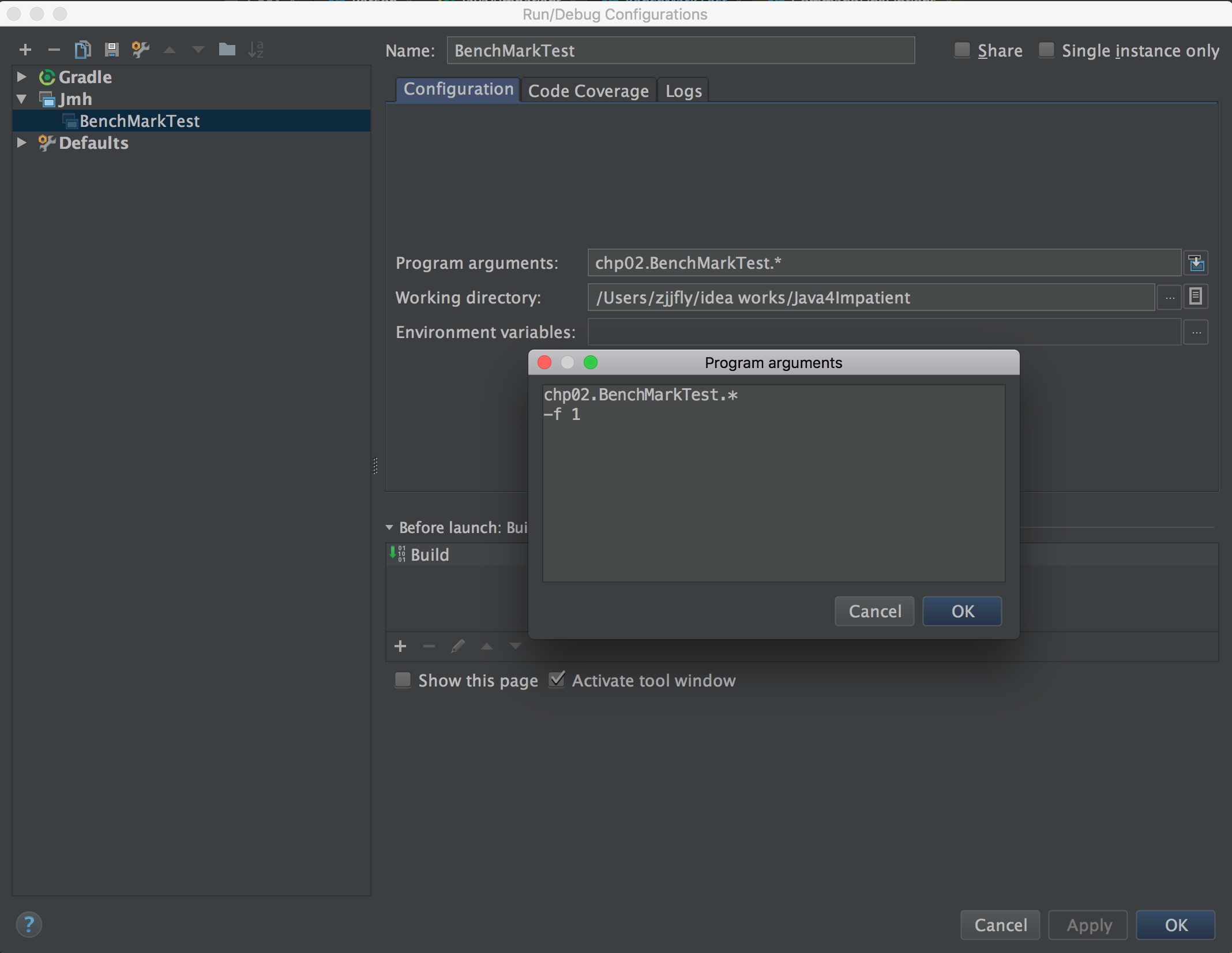
## 配置测试参数
JMH有很多参数可以配置,既可以像上面的代码那样通过注解,也可以通过命令行参数进行配置,JMH用于配置的注解都在`org.openjdk.jmh.annotations`这个package中。如果想知道有哪些命令行参数,可以查看类`org.openjdk.jmh.runner.options.CommandLineOptions`,然后在运行配置中加上相应的参数就可以了。